Fördjupning
Fördjupa dig med hjälp av litteratur och klinisk dokumentation.
Fördjupa dig med hjälp av litteratur och klinisk dokumentation.

Nyligen publicerade studier sammanfattade på ett enkelt sätt för att hjälpa dig att hålla dig uppdaterad på den senaste forskningen inom blåsdysfunktion. Artiklar baserade på vetenskapliga studier är på engelska.
key:global.content-type: Webbinarie
I det här webbinariet kan du lyssna på Dr. Rebecca Haddad som är läkare specialiserad på fysikalisk medicin och rehabilitering med fokus på geriatrik vid Sorbonne-Universitetet i Paris, Frankrike. Hennes kliniska, forsknings- och undervisningsarbete är dedikerat till vård av personer som åldras med funktionsnedsättningar, med särskilt fokus på urinblåsans åldrande.

key:global.content-type: Webbinarie
I det här webbinariet kan du lyssna på Dr. Gianluca Sampogna, urolog/kirurg som arbetar på Spinal Unit, Niguarda Hospital, Milano, ett center för blås-, tarm- och sexuella hälsoproblem hos ryggmärgsskadade patienter. Han är chef för programmet för sexuell hälsa som erbjuder många lösningar från sexuell rådgivning till rehabilitering, från farmakoterapi till kirurgi.

key:global.content-type: Webbinarie
I det här webbinariet kan du lyssna på Dr. Gianna Rodriguez, professor från Michigan, USA. Hon är chef för programmet för ryggmärgsskador (RMS) vid avdelningen för fysisk medicin och rehabilitering (PMR) vid Michigan Medicine i USA.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Den här artikeln utforskar hur åldrandeprocessen påverkar urinblåsan och tarmens funktion hos RMS-patienter och diskuterar behovet av specialiserade behandlingsstrategier.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Den här artikeln sammanfattar de viktigaste utmaningarna och rekommendationerna som identifierats i kliniska riktlinjer (CPG) som styr en åldrande befolkning med ryggmärgsskada. Den lyfter också fram luckor och förbättringsområden i de befintliga riktlinjerna.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
The traditional view of urine sterility has been challenged by the discovery of the urinary microbiome, meaning a mix of bacteria and microorganisms within the urinary tract. This unique relationship between microbes and humans is still not fully understood but has gained a lot of attention in clinical research in the last decade.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
This study provides valuable insights into the experiences of individuals undergoing IC that optimize patient care and support.
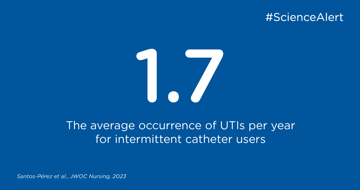
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a leading diagnosis among males. Approximately 100,000 men are treated with transurethral prostate (TURP) surgery each year, making it one of the most common surgical procedures in the United States and several other countries.
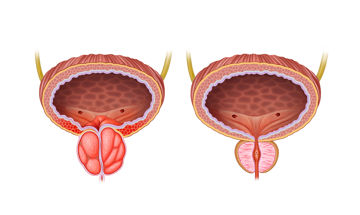
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
At Wellspect HealthCare we take our environmental responsibility seriously. We continuously work to minimize the environmental impact related to our products. We ensure that proper materials are used and all applicable production requirements are followed. For the LoFric catheter, this means that we use a core catheter material with proven low environmental impact as compared to other common catheter materials1 without compromising quality and patient perception.2 3 In fact, the core material of LoFric has been proven to optimize catheter management and reduce discomfort.2
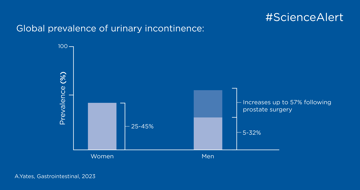
key:global.content-type: Publication Highlight
In this article we sum up the key findings and recommendations of a 2023 study by Bauer et al. which explores intermittent catheterization (IC) by children and adolescent in school settings.

In this publication highlight you can read about the identification, assessment, and treatment of urinary incontinence and bowel control issues.
Keeping up-to-date and determining the veracity of scientific articles and clinical studies can be overwhelming, so we’ve put together a checklist to help you.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Recurrent UTIs in children with neurogenic bladders constitute high risk of leading to severe kidney damage and need to be an area of attention. This study is useful in determining treatments and proactive measures for preventing recurrent UTIs.
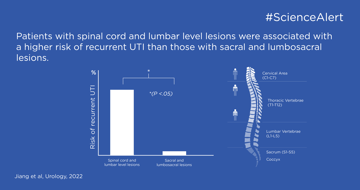
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Catheter associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI) are common in the hospital setting with consequential morbidity and mortality.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
A surprisingly high number of patients reuses catheters intended for single-use every day putting them at risk for unnecessary complications. Single-use hydrophilic catheters for intermittent catheterization lower the risk for short- and long-term complications and are a convenient and preferred choice for many patients.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this publication highlight you will learn more about autonomic dysreflexia (AD) an how to manage an AD episode.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this publication highlight you can read more about how to evaluate neurogenic bladder and bowel dysfunction with a patient-centric tool, goal attainment scaling, to individualize management.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this publication highlight you can read about how constipation impacts urogenital symptoms in women.
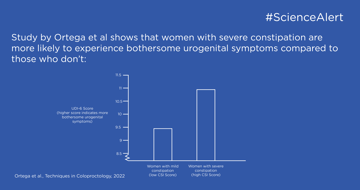
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
A surprisingly high number of patients reuses catheters intended for single-use every day putting them at risk for unnecessary complications. Single-use hydrophilic catheters for intermittent catheterization lower the risk for short- and long-term complications and are a convenient and preferred choice for many patients.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
The no-touch technique includes use of a catheter constructed for introduction without touch by the user’s hands.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Bladder management with intermittent catheterization is associated with complications. The most severe and common one is UTI. Single-use, hydrophilic-coated catheters lower the risk of UTIs and have been reported as both convenient and the preferred choice for people who rely on intermittent catheterization as their bladder management.1 As a result, hydrophilic-coated catheters are identified as a cost-effective contributor in UTI prevention.2

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
For those who cannot empty their bladder the normal way, intermittent catheterization is the therapy of choice to maintain urethral health.
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Bladder instillation is used for local administration of drugs into the bladder. This is used for treatment of interstitial cystitis and cancer, for example. Drugs are being delivered by catheters and a hydrophilic-coated surface such as that of the LoFric catheters reduces the risk for trauma associated with instillation therapy.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Read about urethral strictures, treatment and studies.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Patient adherence plays a key role in a successful and cost-effective catheterization treatment. A patient who feels part of the decision-making, in control of his options and how they work with his lifestyle is more inclined to stick with his therapy and subsequently experience a good clinical outcome.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Urine often has a high concentration of particles and low content of water. This is referred to as high osmolality. Urine osmolality has a direct effect on catheter lubrication and plays an important role for people who use hydrophilic catheters. Catheters with a surface osmolality in balance with urine is key to reducing withdrawal friction.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
A lubricated catheter is recommended to reduce damage to the urethra and lower the risk of hematuria which is a common complication. A cross-over study comparing different hydrophilic catheters showed an even lower frequency of hematuria in patients who chose LoFric.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Extensive studies support scientific literature claiming that use of hydrophilic catheters reduce urethral trauma and urinary tract infections. This in turn can minimize the need for antibiotics. Because of these benefits, we now know that hydrophilic catheters are one of the most cost-effective ways to prevent long term urological complications in general and UTI in particular.
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Single-use hydrophilic catheters were developed in the early eighties to address long-term complications of intermittent catheterization as seen when reusing plastic catheters with add-on lubrication.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
According to WHO the problem of antimicrobial resistance is so serious that it threatens our modern healthcare system
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Available clinical evidence supports the strategy to always consider intermittent catheterization as the first therapeutic choice, before considering the use of an indwelling catheter. Intermittent catheterization is the first therapeutic choice and is a safer bladder management method than both urethral and suprapubic indwelling catheters. Intermittent catheterization is central to reduce morbidity related to renal failure and neurogenic bladder dysfunction.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Bladder management with intermittent catheterization is associated with complications. The most severe and common one is UTI.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
With more than 30 years on the market, LoFric has been used and documented in several ways.

Nyligen publicerade studier sammanfattade på ett enkelt sätt för att hjälpa dig att hålla dig uppdaterad på den senaste forskningen inom tarmdysfunktion. Artiklar baserade på vetenskapliga studier är på engelska.
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Take part of clinical evidence that speaks to the improved outcomes of using TAI in pediatric patients when coupled with an individualized approach upon initiation of TAI.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
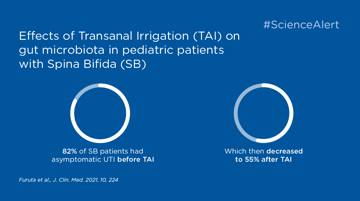
Transanal irrigation's influence on gut microbiota could have a positive effect on the immune system and contribute to reduced UTIs, as per this clinical study by Futura et. al.
key:global.content-type: Webbinarie
I det här webbinariet kan du lyssna på Dr. Rebecca Haddad som är läkare specialiserad på fysikalisk medicin och rehabilitering med fokus på geriatrik vid Sorbonne-Universitetet i Paris, Frankrike. Hennes kliniska, forsknings- och undervisningsarbete är dedikerat till vård av personer som åldras med funktionsnedsättningar, med särskilt fokus på urinblåsans åldrande.

key:global.content-type: Webbinarie
I det här webbinariet kan du lyssna på Dr. Gianluca Sampogna, urolog/kirurg som arbetar på Spinal Unit, Niguarda Hospital, Milano, ett center för blås-, tarm- och sexuella hälsoproblem hos ryggmärgsskadade patienter. Han är chef för programmet för sexuell hälsa som erbjuder många lösningar från sexuell rådgivning till rehabilitering, från farmakoterapi till kirurgi.

key:global.content-type: Webbinarie
I det här webbinariet kan du lyssna på Dr. Gianna Rodriguez, professor från Michigan, USA. Hon är chef för programmet för ryggmärgsskador (RMS) vid avdelningen för fysisk medicin och rehabilitering (PMR) vid Michigan Medicine i USA.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Den här artikeln utforskar hur åldrandeprocessen påverkar urinblåsan och tarmens funktion hos RMS-patienter och diskuterar behovet av specialiserade behandlingsstrategier.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
A cost-effectiveness analysis of Navina Smart on adult patients affected by neurogenic bowel dysfunction.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Transanal Irrigation (TAI) is known to be a successful therapy to treat LARS, and in this study, Orlandi et al explore the use of TAI as a treatment option for women with endometriosis who experience LARS-like symptoms.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Take part of clinical data on transanal irrigation as a mean to manage neurogenic bowel in the pediatric population with Spina Bifida
key:global.content-type: Publication Highlight
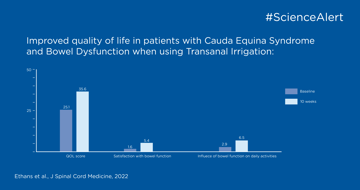
In this publication highlight you can read about how to manage bowel dysfunction in individuals with cauda equina syndrome.
In this publication highlight you can read about the identification, assessment, and treatment of urinary incontinence and bowel control issues.

Keeping up-to-date and determining the veracity of scientific articles and clinical studies can be overwhelming, so we’ve put together a checklist to help you.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this publication highlight you will learn more about autonomic dysreflexia (AD) an how to manage an AD episode.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this publication highlight you can read more about how to evaluate neurogenic bladder and bowel dysfunction with a patient-centric tool, goal attainment scaling, to individualize management.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this publication highlight you can read about how constipation impacts urogenital symptoms in women.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this publication highlight you can read about pediatric constipation causes, impact and management.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this summary you can read about what a neurogenic bowel is and goals and recommendations for treatment.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
This is a summary of the published article Long-term efficacy and safety of transanal irrigation in multiple sclerosis by Passananti et al. 2016

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
In this science article a combined retrospective and cross-sectional survey study investigates chronic idiopathic constipation in children and bowel regimen with bowel irrigation, also called transanal irrigation (TAI).

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Bowel problems in children are common, up to 29% of children can be affected by functional constipation and functional fecal incontinence.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Summary of first data on Navina Smart
key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Transanal irrigation (TAI) is a well-documented and safe bowel management therapy. Today, compliance is the major issue with TAI therapy, and may be improved through greater knowledge of which patient is best suited for TAI. Patient training and close follow up with digital support during start up may also increase compliance.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Defecation disorders are common in conditions affecting the nervous system, such as spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, spina bifida and severe Parkinson’s disease, and have great impact on self-esteem, personal relationships and social life

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Fecal incontinence (FI) means involuntary loss of rectal content such as solid and liquid stool, mucus or flatus. FI is not a diagnosis but a symptom. It is considered a stigmatizing condition, and fear of having an accident in public restricts the social and working life for those who experience it. Although there are many treatment options, their long-term efficacy is poorly investigated.

key:global.content-type: Artiklar
Bowel dysfunction is surrounded by misconceptions and taboos that may interfere with treatment and that may result in self-medication not always innocuous to the patient care.
